The Internet of Things has completely transformed our way of life. As per Statista projections, there will be around 29 bn. connected devices by 2030. However, as their number constantly grows, there emerge serious concerns. The possibility of breaches and hacking grows with the massive data flows. However, blockchain in the IoT can solve many problems. By taking advantage of its decentralized and encrypted characteristics, sensor data can be safeguarded in tamper-proof ledgers that are exceptionally challenging for cybercriminals to manipulate.
Let’s see how blockchain in the IoT can enhance the security of networks worldwide and single out the challenges that need to be addressed before its widespread adoption. With proactive measures, decentralized technology might resolve vulnerabilities and transform various sectors of the modern economy.

Table of Contents
Blockchain in the IoT: a brief introduction
Blockchain technology represents a decentralized ledger system, facilitating secure, transparent, and distributed transaction recording. Its remarkable promise shines especially bright within the Internet of Things, where devices generate vast amounts of data necessitating secure and reliable storage and transmission.
Blockchain networks consist of globally distributed P2P nodes that jointly follow predefined protocols to validate transactions. All information is kept in cryptographically chained blocks that are highly tamper-resistant.
Blockchain ensures IoT data integrity by making it nearly impossible for criminals to overwrite or manipulate records. Cryptography ensures robust end-to-end encryption as the data moves between devices.
Smart contracts can automate data sharing and permissions in a transparent way using predetermined rules written into code. For instance, a connected vehicle can be programmed to unlock only for authorized users based on blockchain verification.
However, there are still challenges in combining these innovations. Performance and storage limitations need to be addressed before blockchain is ready for large-scale IoT data. But as technologies advance, we will undoubtedly see connected systems protected as securely as never before.
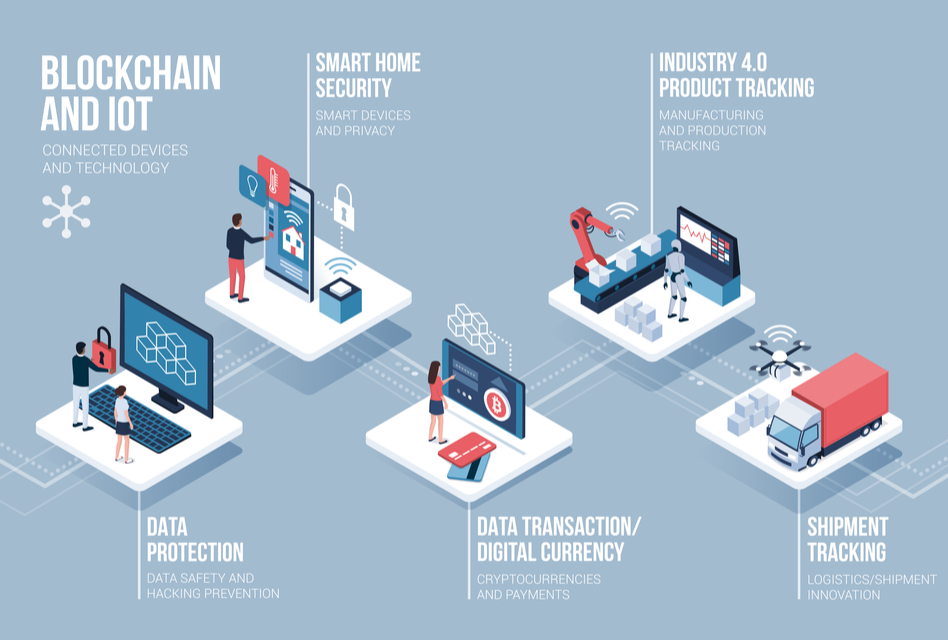
How blockchain can be used in the IoT
The opportunities in this area are impressive, and we will definitely see more innovative scenarios of use. Let’s see what is available now.
Operational maintenance
Modern sensors can constantly monitor the health and performance of industrial equipment like engines, generators, and elevators. This real-time telemetry data can be recorded on a decentralized network to create comprehensive maintenance logs that are transparent and tamper-proof. In case of any concerns, these immutable logs help technicians to rapidly diagnose problems. Maintenance records can also be seamlessly shared with regulatory bodies to demonstrate compliance.
In general, blockchain streamlines operational maintenance by establishing a single source of truth for asset health data and maintenance history across industries like manufacturing, energy, and construction.
Freight transportation
Freight shipments often involve handoffs between multiple parties like manufacturers, land carriers, customs brokers, and ocean liners. This complexity can lead to disputes, delays, and a lack of accountability. Blockchain enables real-time tracking of shipping containers throughout their journey by recording key data points like location, temperature, certifications, and chain of custody on a shared ledger. Smart contracts can automate payments and other workflows when predefined conditions are met. With end-to-end transparency, all stakeholders can pinpoint issues rapidly to prevent spoilage, delays, and disputes. This innovative approach thus brings unprecedented efficiency, security, and collaboration to global freight supply chains.
Automotive industry
The automotive sector is rapidly adopting IoT sensors to enable breakthroughs like autonomous driving, usage-based insurance, and vehicle health monitoring. Integrating blockchain provides tamper-proofing of telemetry data and ensures its secure sharing between OEMs, insurers, repair shops, and other ecosystem partners. Smart contracts can execute financial transactions as vehicles autonomously avail services like refueling or toll payments. Vehicle identities validate credentials to authorize access requests. As a result, businesses and users see strengthened data integrity, automation, security, and transparency, all of which are pivotal for success.
Pharmacy
Pharmaceuticals face major threats from counterfeit drugs that put patients’ lives at risk globally. Modern tech solutions can secure the pharma supply chain by tracking medicines from factories to pharmacies. Scannable QR codes can link medications to their blockchain records that show provenance across each step. If a drug is diverted or tampered with, it would be immediately evident. Regulators can also audit the ledger to verify quality compliance and distribution authorizations. The ability to prevent falsified, substandard, and unauthorized medicines can literally save millions of lives while protecting pharmaceutical brands.
Smart homes
In smart homes, security cameras, thermostats, and appliances are controlled through a central hub. This single point of failure poses risks like server outages and hacking. If IT professionals implement decentralized smart home networks, devices will communicate peer-to-peer based on immutable protocols. Thus, property owners will gain full control of security and permissions without relying on a centralized system. Usage data can be monetized securely using blockchain-based micropayments. With automation and radical transparency, smart homes reach the next level.
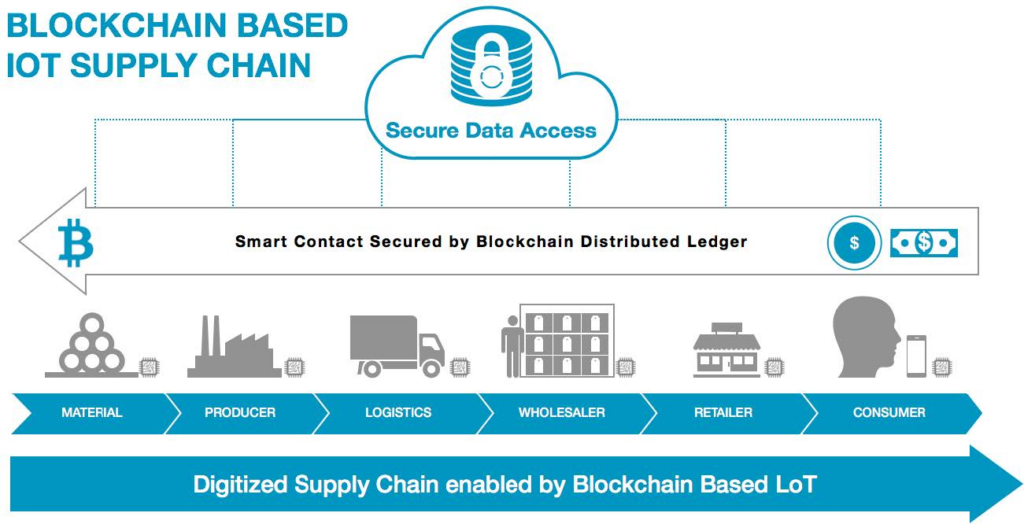
Supply chain management
Global supply chains involve extensive documentation and data exchange between importers, exporters, regulators, and logistics providers. This complexity reduces accountability and exposes systems to single points of failure. Therefore, a transparent, shared record of truth across the entire supply chain network is essential. The need for manual verification and paper trails is eliminated as all partners can trust the data on the immutable ledger. From aircraft parts to automotive components, innovative technology enables real-time supply chain tracking and process integrity across industries.
Insurance
Insurers face immense inefficiencies in claims processing, fraud detection, and evaluating policies. IoT data combined with smart contracts can automate policy underwriting, speed up claims, and prevent fraud. Usage-based insurance leverages real-time telemetry from devices like cars and wearables to dynamically calculate premiums based on observed risk profiles. Blockchain delivers complete transparency for insurers to accurately price policies while streamlining administration.
Sharing economy
Sharing economy allows underutilized assets like houses, vehicles, and equipment to be rented out peer-to-peer. However, this requires trust between strangers mediated by central platforms. Blockchain enables decentralized sharing networks where IoT-enabled assets can directly transact with users through smart contracts in a trusted manner without intermediaries. Usage can be accurately tracked to calculate dynamic pricing, automated payments, and deposit refunds. Reputation systems prevent misuse. For instance, an electric scooter could detect authorized riders through reliable verification and lock out unauthorized usage. Innovative technologies working together can fuel sharing economy innovation and growth.
Water management
Pioneering sensors can monitor the quality and consumption of water across municipal pipelines, treatment facilities, and homes. By recording this data on a secure block, tampering or denial of leakages and contamination can be prevented. Smart systems can autonomously shut off pipes or alert authorities when anomalies are detected. Usage can be accurately tracked to implement consumption-based billing. Regulators can independently verify compliance through a transparent and immutable ledger. This enhances the reliability, security, and accuracy of mission-critical water management infrastructure.
Agriculture
This sector can be massively enhanced using IoT sensors in fields to monitor soil conditions, crop growth, equipment performance, and other parameters in real time. Recording this data on tamper-proof ledgers secures E2E traceability across the food supply chain. Farmers can share data with distributors, retailers, and regulators to build trust and compliance. Smart contracts enable crop insurers to automate payouts when environmental conditions measured by IoT sensors trigger claim events. Consumers can validate the origin, safety, and handling of products by scanning blockchain-linked QR codes. All this enables transparency, automation, and optimization across agricultural ecosystems.

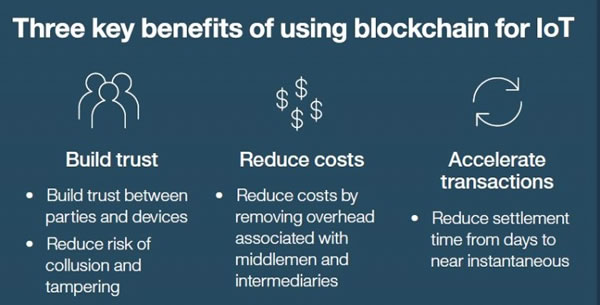
Advantages of blockchain in the IoT
When working together, these pioneering technologies offer a range of benefits that can take the security of workflows and overall performance to the next level.
- Lower expenses
IoT systems require massive centralized cloud infrastructure to store, process, and analyze all the data. Decentralized architecture eliminates these expensive centralized nodes. Instead, DLT allows devices to communicate and transact P2P in a scalable way at a fraction of the cost.
- Enhanced protection
Advanced cryptographic principles are used in a secure ledger to prevent tampering. Timestamps and hashes ensure the immutable recording of all transactions. A decentralized database does not have a single point of failure. This layered security model protects connected systems from increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
- Faster data exchange
Validating transactions is fast due to consensus protocols and distributed processing. This enables real-time data sharing between IoT devices to optimize system efficiency. Latency is reduced without compromising security.
- Automation with smart contracts
When certain conditions are met, these programmable scripts execute automatically. This allows interconnected devices to autonomously manage transactions through rules encoded in a blockchain. Manual interventions are minimized.
- Supply chain monitoring
Ledger technology provides E2E traceability of food, medicine, electronics, etc. This brings perfect transparency and accountability globally, with billions of data points.
- New revenue models
Micropayments between devices open up new monetization opportunities. Users can pay for exact data consumption while sensors can seamlessly earn revenue. This drives innovation in IoT business models.
By tapping into blockchain’s potential, the possibilities for optimized, secure, and decentralized IoT networks are endless. The technology can help the IoT truly realize its monumental promise.
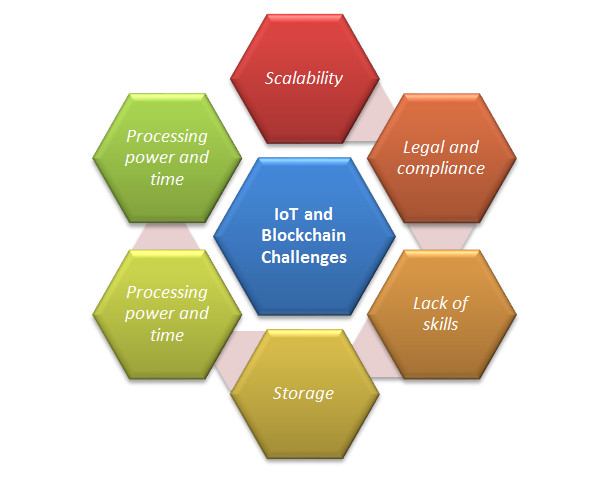
Adoption barriers
Although both tech innovations possess immense potential, integrating them involves significant technical and design challenges:
- Scalability
Public ledgers have limits on transaction processing speed and data storage. With billions of connected devices expected, the scalability of a decentralized database becomes a serious concern. Solutions like sharding, state channels, and directed acyclic graphs are being explored.
- Interoperability
There are many competing decentralized platforms and protocols. Getting different implementations to interact seamlessly is difficult. Standards organizations are defining frameworks to enable interoperability.
- Energy usage
The proof-of-work consensus is energy-intensive. Newer protocols like proof-of-stake and proof-of-authority dramatically cut energy needs.
- Smart contract security
While smart contracts enable automation, bugs can lead to exploitation. Rigorous testing, audits, and formal verification techniques are indispensable to minimize vulnerabilities.
- Privacy tradeoffs
Public ledgers offer transparency but lack privacy. Private ones provide more control over data sharing but reduce decentralization. Balancing transparency with privacy is vital.
- Talent shortage
Both tech innovations still have a long way to develop and strengthen their capacities. Therefore, more skilled specialists are needed. Investing in training and partnerships is essential to assemble competent teams.
- Immature ecosystem
Standards, tools, and infrastructure for blockchain in the IoT haven’t been fully elaborated yet. Production deployments will take time to stabilize and optimize. But the pace of innovation is rapid.
Overcoming these barriers will require continued research and development.
DLT as the backbone of the next-generation IoT
In the future, many industries will enhance their potential thanks to the IoT. However, this requires overcoming vulnerabilities from centralized designs.
Blockchain gives the necessary strengths and mechanisms to secure a steady and continuous growth of the global IoT ecosystem. As IoT expands into critical infrastructure, many professionals see blockchain as mandatory. It enables trustless device coordination at a global scale.
There are still challenges in integrating blockchain and IoT. But steady progress is underway. Blockchain can allow the IoT to finally fulfill its vast promise through securely decentralized machine economies.
Wrapping up
As the IoT continues to evolve, the accompanying risks related to security, privacy, and centralized control threaten to derail its immense benefits. DLT has immense capacities to address potential problems effectively. Though integration challenges around scalability, energy usage, and interoperability exist, we are steadily inching toward a future powered by secured and optimized networks.
Over time, traditional IoT systems will transition to incorporate blockchain for ensuring data integrity, managing access, and automating processes, thereby unlocking the boundless potential of interconnected devices in numerous sectors while upholding trust and security. We find ourselves on the brink of a revolutionary shift, where both technologies lay the foundation for a multitude of opportunities. Prominent Internet of Things application development companies are dedicated to turning this vision into a tangible reality.

